Product Inspection Process for Aluminum Cylinder Heads
High-Quality Assurance from Raw Material to Final Packaging
1. Incoming Material Inspection
Aluminum Alloy Composition Analysis
- Use spectrometers to analyze the aluminum alloy grade (e.g., A356.2, AC4B)
- Check material certificates and traceability of furnace batch numbers
Auxiliary Material Inspection
- Check batch numbers, appearance, drying quality, and flowability of coatings, sand cores, and chills
2. Post-Casting Inspection
Visual Inspection
- Check for porosity, slag inclusion, cracks, deformation, and cold shuts
- Verify the profile and dimensional completeness according to drawings
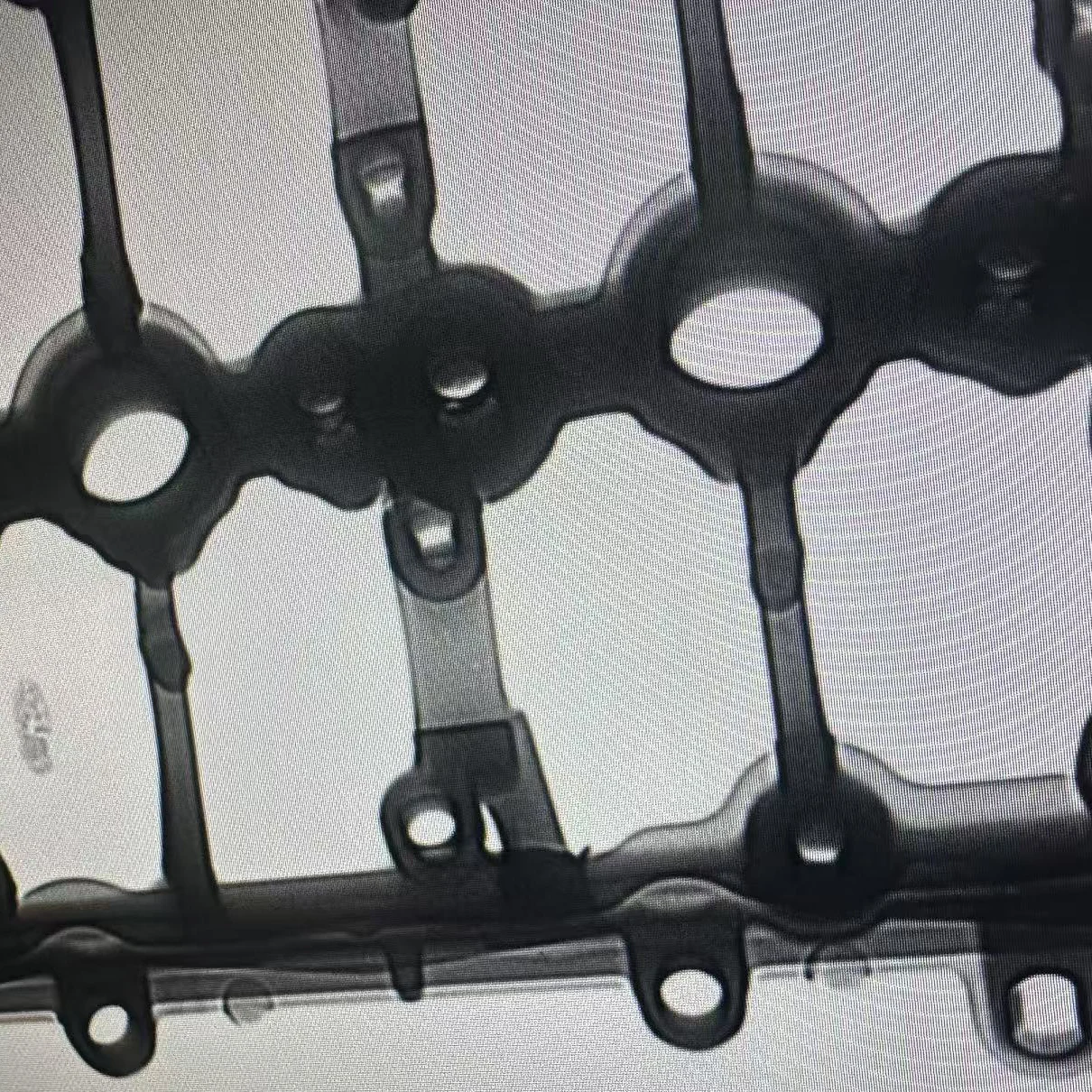
X-ray Defect Testing
- Conduct non-destructive testing (NDT) on critical areas like combustion chambers, water, and oil passages
- Evaluate internal defects such as shrinkage cavities, sand holes, and inclusions
3. Post-Machining Inspection
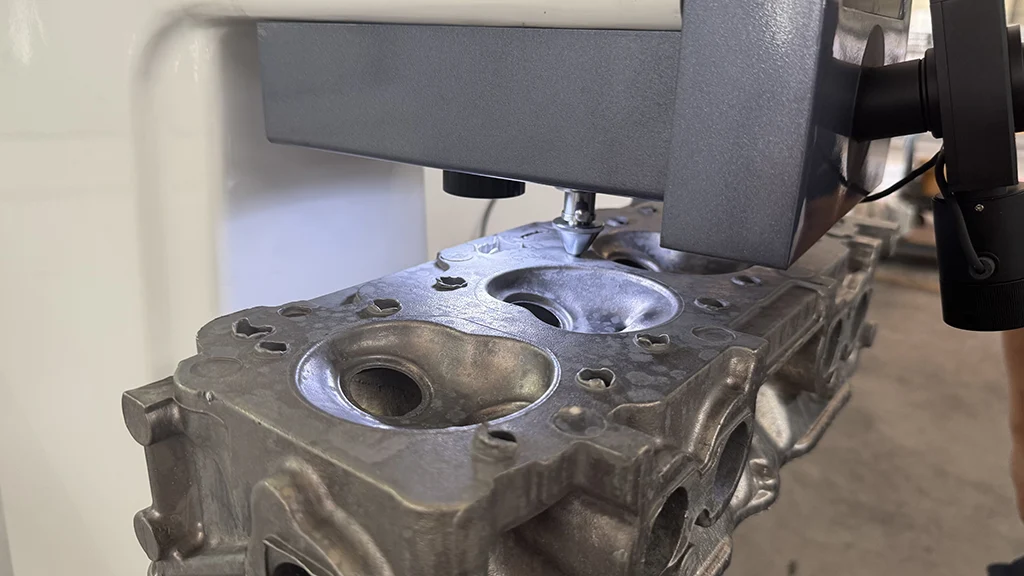
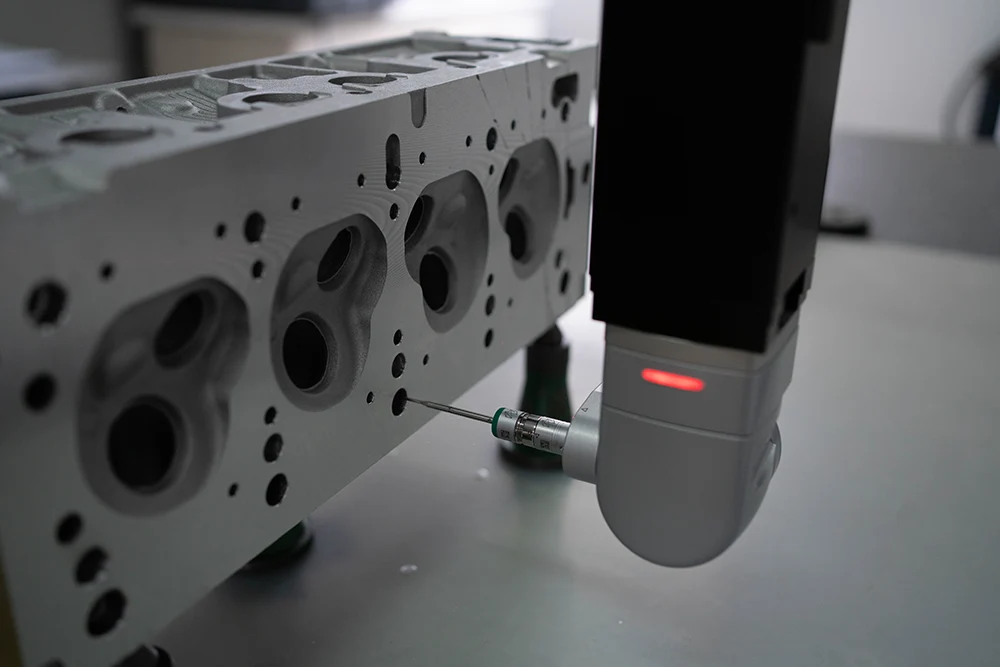
Dimensional Inspection
- Use CMM, calipers, and micrometers to check critical dimensions
- Inspect valve guide holes, valve seat bores, camshaft journals, and head flatness
Thread Hole Inspection
- Check threads with go/no-go gauges
- Ensure concentricity and thread integrity
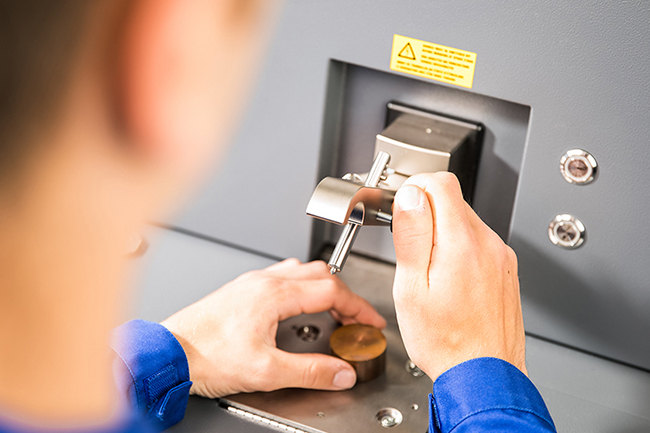
Hardness Test
- Perform Brinell or Rockwell hardness testing to confirm heat treatment or natural aging results
4. Leakage & Pressure Test
Water Jacket Air Pressure Test
- Inject 0.5-1.0MPa of air pressure, hold for 1 minute, and check for leaks or bubbles
Oil Passage Pressure Test
- Simulate oil pathways using fixtures, then conduct pressure holding and sealing tests
5. Final Appearance & Cleanliness Inspection
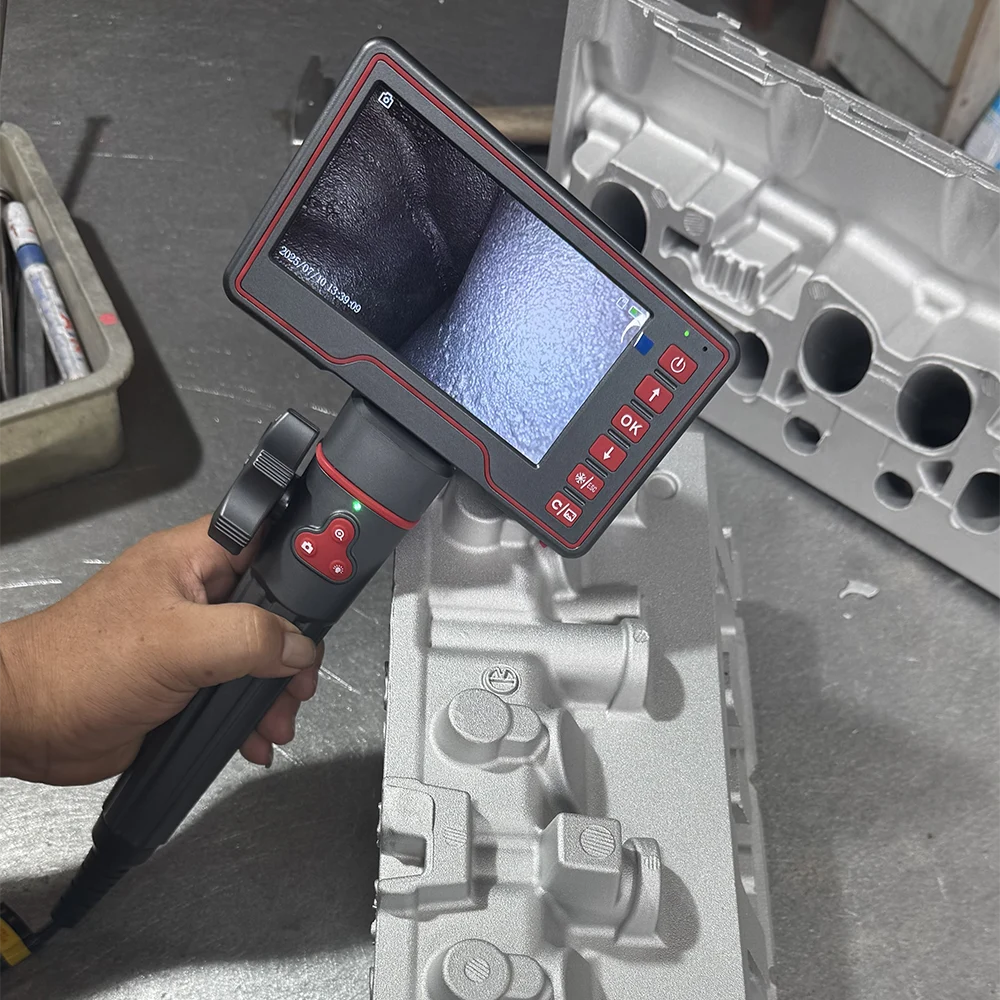
Cleanliness Check
- Inspect for residual metal chips or sand inside the casting
- Use endoscopes or cleanliness analysis devices to detect contamination
Surface Treatment Confirmation
- Verify deburring, sandblasting, passivation, and coating quality
- Check if labeling, batch number, and anti-rust protection are in place
6. Final Pre-Packaging Inspection
- Inspect product model, batch number, and accessory completeness as per shipping standards
- Verify traceability via QR codes, laser marking, or serial numbers
- Ensure packaging materials are clean, pressure-resistant, and moisture-proof
- Include certificates of conformity and packing list before shipment
Remarks
- One sample from each batch should be retained for traceability
- Inspection records must be archived for no less than three years
- Custom test plans available upon client request
Product assembly testing and road testing
1. Cylinder Head Assembly Testing Procedure
Pre-Inspection of Components
- Inspect valves, valve guides, valve seats, springs, oil seals, camshaft, and bushings
- Confirm material certificates and hardness test reports
- Ensure dimensional accuracy per technical drawings
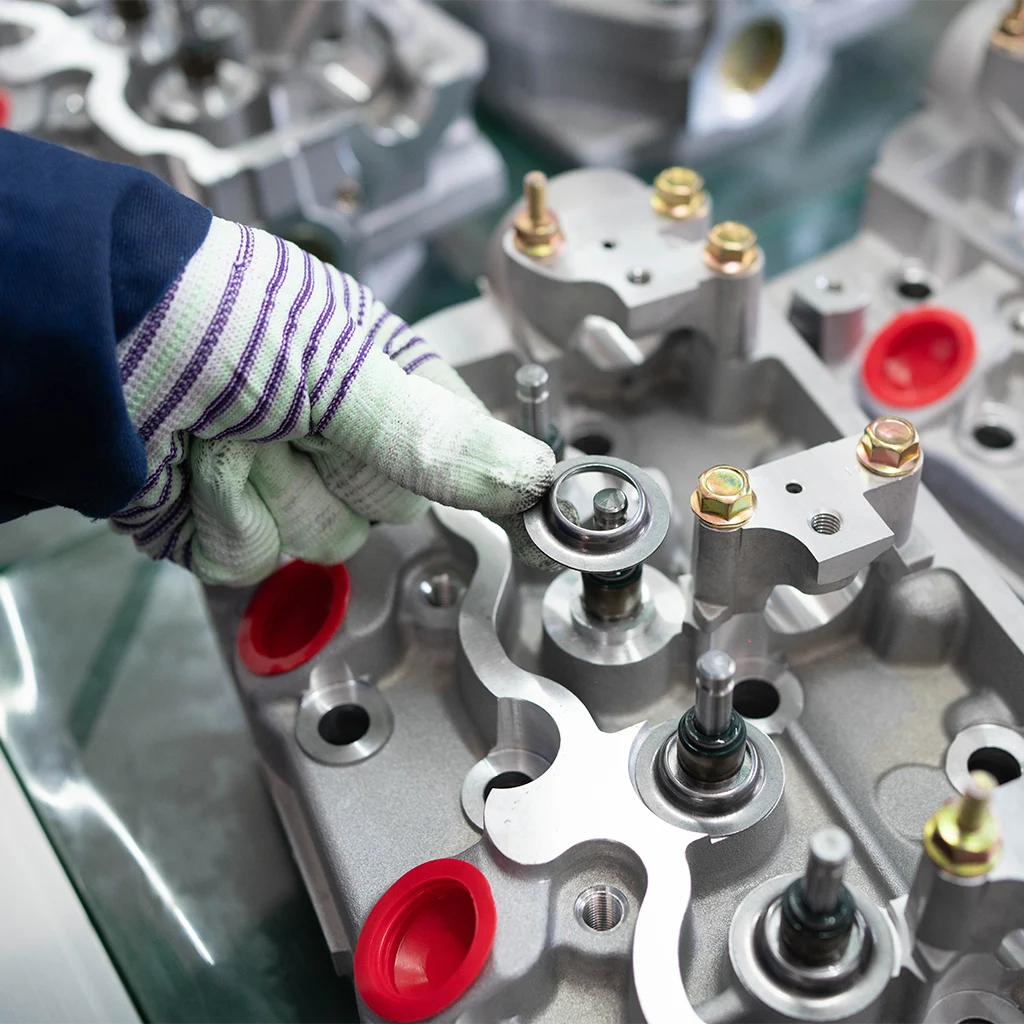
Precision Assembly
- Install valve group (valve, spring, retainer, locks)
- Press-fit valve stem seals carefully to avoid damage
- Insert valve guides and check clearance (g., 0.02-0.05 mm)
- Perform valve sealing test (g., kerosene leak test or vacuum test)
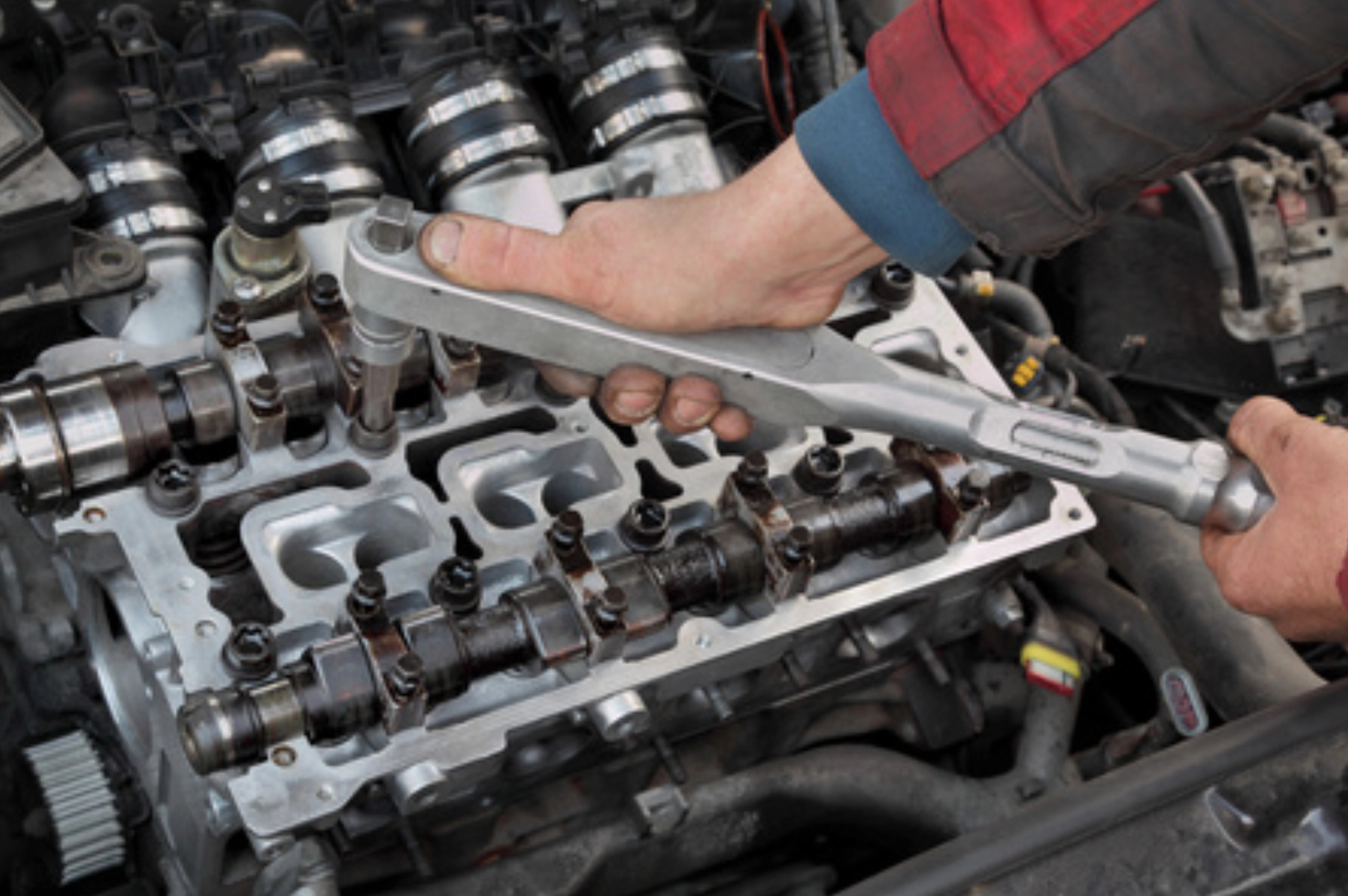
- Assemble camshaft and bearing caps, tighten bolts per torque and sequence specs
- Adjust valve clearance if applicable
Dynamic Function Test
- Rotate camshaft manually to ensure smooth movement
- Check valve timing and spring return
- Perform pressure testing:
- Air pressure test
- Oil passage pressure test
- Run vacuum or pressure leak test on assembled head
2. Cylinder Head Road Test Procedure (for Aftermarket Units)
Trial Installation & Cold Start Check
- Install cylinder head assembly on engine using OEM torque sequence and specifications
- Fill coolant and engine oil
- Start engine cold, observe for eaks, abnormal noise, and idle stability
Warm-Up Test (Idle and Load)
- Bring engine to operating temperature ( 90-95°C)
- Test under idle and increased RPMs
- Monitor:
- Valve noise
- Valve clearance behavior
- Oil pressure and coolant temperature
- If no anomales after 20-30 minutes, proceed to road test
Road Simulation Test
Recommended Duration: 500-3,000 km (depending on project scope)
- Driving Conditions:
- Urban driving: Stop-and-go traffic, idle time
- Highway driving: Constant speed at higher RPM
- Uphill/High-load segments: Test combustion chamber temperature resilience
- Rapid acceleration/deceleration: Test oil supply, valve spring response
- Monitoring Points:
- Coolant and oil levels
- Smoke emissions (white = coolant, black = fuel, blue = oil)
- Unusual engine sounds
- Overheating or temperature spikes
- Check engine lights or OBD readings
Post-Test Disassembly & Analysis
- Remove the cylinder head and inspect:
- Valve and seat condition (burning, deformation)
- Valve guide wear
- Gasket impressions and sealing effectiveness
- Flatness of the head base
- Any signs of cracks, corrosion, or oil/water leakage